Operation of the Vane Pump: Working Principle, Components, and Applications
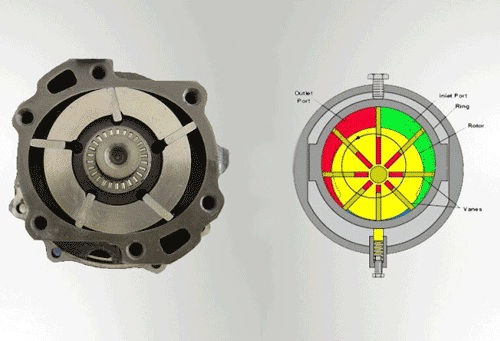
The operation of the vane pump is an essential concept in fluid power systems. This technology is part of the broader vane type pump family, which also includes rotary vane vacuum pumps widely used in industrial and scientific applications. In the automotive world, vane pumps play a critical role in hydraulic steering systems, automatic transmissions, and air conditioning compressors.
By understanding the hydraulic pump vane mechanism and the role of the vane rotary movement, engineers and technicians can better diagnose, maintain, and optimize hydraulic systems.
What is a Vane Type Pump?
A vane type pump is a positive displacement pump that uses sliding vanes to move fluid. The vanes are mounted in a rotor that spins inside a cam-shaped cavity. As the rotor turns, the vanes extend and retract, creating chambers that draw in and expel liquid.
There are two main categories:
- Balanced Vane Pumps – Designed to reduce side loads and improve efficiency.
- Unbalanced Vane Pumps – Simpler in design but subject to uneven pressure distribution.
💡 In both types, the hydraulic pump vane is the critical component responsible for trapping and transferring fluid.
Design and Construction of a Balanced Vane Pump
A balanced vane pump features dual inlet and outlet ports placed opposite each other, which balances hydraulic forces. This design reduces wear and prolongs service life compared to an unbalanced design.
Main Components:
- Rotor – The rotating part that holds the vanes.
- Vanes (Hydraulic Pump Vanes) – Sliding elements that maintain contact with the inner cam ring.
- Cam Ring – Provides the oval contour that controls vane movement.
- Inlet and Outlet Ports – Allow fluid to enter and leave.
- Casing – Houses and protects the pump assembly.
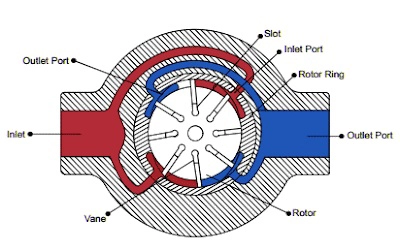
The vane rotary motion inside the oval ring ensures that the pump continuously generates suction and discharge phases.
Working Principle of a Vane Rotary Pump
The vane rotary mechanism operates through centrifugal and hydraulic forces.
Step-by-Step Functioning:
- Rotor Rotation – The driveshaft spins the rotor.
- Vane Extension – Hydraulic pump vanes slide outward and follow the contour of the cam ring.
- Chamber Expansion – As the rotor turns, spaces between vanes enlarge, creating suction.
- Fluid Intake – Liquid enters through the inlet ports, filling the vacuum.
- Chamber Contraction – As the rotor continues, chambers shrink, compressing the fluid.
- Fluid Discharge – Compressed liquid exits through the outlet ports.
- Cycle Repeat – This process occurs twice per revolution in a balanced vane pump.
This principle is also the basis of rotary vane vacuum pumps, where instead of moving liquids, the vanes create and maintain a vacuum.
Advantages of Vane Type Pumps
- Low Noise Operation – Suitable for automotive and industrial use.
- Constant Flow Delivery – Stable performance in hydraulic circuits.
- Compact Size – The vane rotary design saves space.
- Durability – Long life with balanced port placement.
- Versatility – Applicable to both hydraulic pump vane systems and vacuum pumps.
Disadvantages of Vane Pumps
- Sensitive to contamination and dirt.
- Limited to medium-pressure applications.
- Hydraulic pump vanes may wear and need replacement.
- Not ideal for abrasive or highly viscous fluids.
Applications of Vane Pumps
Automotive Applications
- Power Steering Systems – Smooth control using balanced vane design.
- Automatic Transmissions – Provide oil circulation and pressure.
- Air Conditioning Compressors – Often based on rotary vane pump principles.
Industrial Applications
- Hydraulic Systems – Forklifts, presses, and injection machines.
- Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps – Used in refrigeration, medical suction equipment, and laboratory instruments.
- Fuel Handling – Aviation fuel and diesel transfer.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the difference between a vane type pump and a rotary vane vacuum pump?
A vane type pump moves liquids in hydraulic systems, while a rotary vane vacuum pump creates vacuum pressure for air and gases.
Q2: How does a hydraulic pump vane work?
The vane slides in and out of the rotor slots, trapping and transporting fluid as chambers expand and contract.
Q3: What industries use vane rotary pumps?
They are common in automotive hydraulics, refrigeration, medical devices, and laboratory vacuum systems.
Q4: Why is the balanced vane pump more efficient?
Because the inlet and outlet ports are placed opposite each other, balancing hydraulic forces and reducing wear.
Conclusion
The operation of the vane pump whether in automotive systems or as part of rotary vane vacuum pumps—is based on the same fundamental principle: vane rotary movement creating suction and discharge. The hydraulic pump vane is at the heart of this mechanism, providing durability, efficiency, and reliability.
For engineers, mechanics, and students, understanding vane pumps means unlocking knowledge that applies across hydraulics, automotive technology, and vacuum systems.





